
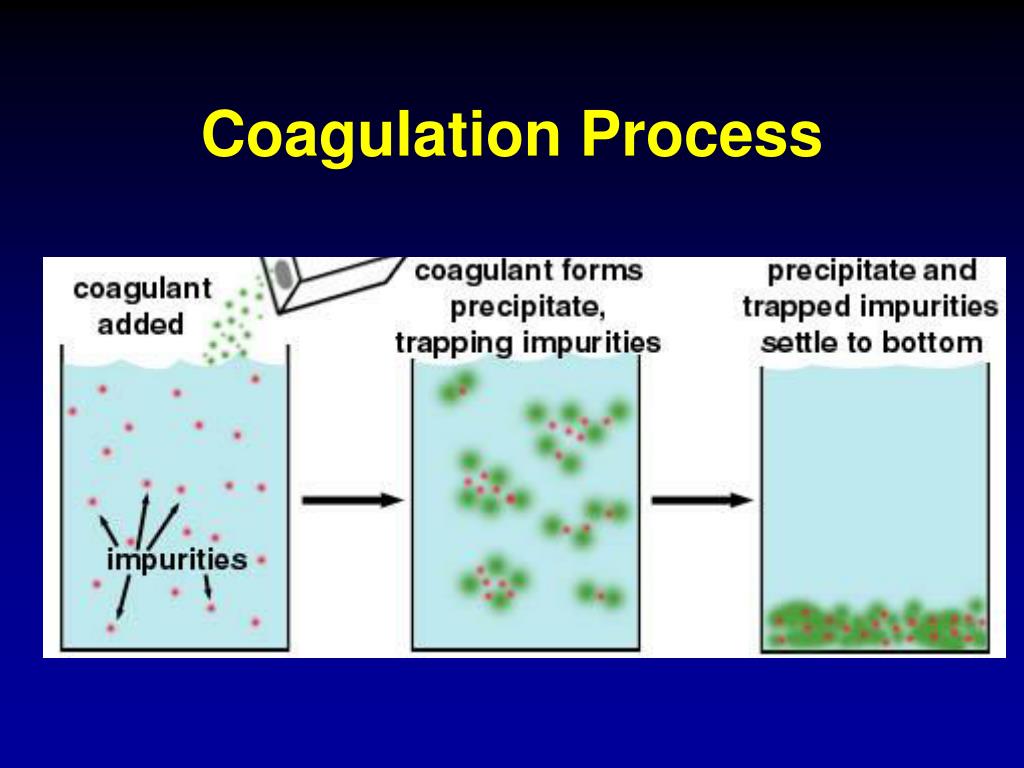
Because precipitation usually occurs in a solution that is rich in dissolved solids, the initial precipitate is often impure.
#Define precipitate form coagulation free
In addition to having a low solubility, the precipitate must be free from impurities.

For example, the K sp of PbSO 4 is 2 × 10 –8 in H 2O and 2.6 × 10 –12 in a 50:50 mixture of H 2O and ethanol. The poorer solvating ability of non-aqueous solvents, even those which are polar, leads to a smaller solubility product. A precipitate’s solubility is generally greater in an aqueous solution because of water’s ability to stabilize ions through solvation. When solubility is a concern, it may be possible to decrease solubility by using a non-aqueous solvent. Because the solubility of CaF 2 spans several orders of magnitude, its solubility is shown in logarithmic form. Note that the solubility of CaF 2 is independent of pH for pH levels greater than 4.17, and that its solubility increases dramatically at lower pH levels where HF is the predominate species.

The predominate form of fluoride in solution is shown by the ladder diagram along the x-axis, with the black rectangle showing the region where both HF and F – are important species. The solid blue curve is a plot of equation 8.11. At more acidic pH levels, the solubility of CaF 2 increases because of the contribution of reaction 8.9.įigure 8.2 Solubility of CaF 2 as a function of pH. When the pH is greater than 4.17, the predominate species is F – and the solubility of CaF 2 is independent of pH because only reaction 8.8 occurs to an appreciable extent. Depending on the solution’s pH, the predominate form of fluoride is either HF or F –. Problem 4 in the end-of-chapter problems asks you to show that equation 8.11 is correct by completing the derivation.įigure 8.2 shows how pH affects the solubility of CaF 2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
